In this tutorial, we will go over how to log data to weights & biases (wandb).
Weights & Biases (wandb) server is a commercially hosted service and thus requires an account to be made in wandb.com.
An alternative is a self-hosted server is available and is distributed as docker and can be started using
docker run --rm -d -v wandb:/vol -p 8080:8080 --name wandb-local wandb/local
This creates a server at port 8080 and can be accessed via a browser on localhost:8080. It will prompt you to create an account and then can be used to create a local account to log in.
The data is stored in the docker volumes locally (usually /var/lib/docker/volumes/wandb/_data). The docker server is running in the background and to stop it we can use docker stop wandb-local.
Note that weights & biases does have a free tier for individuals and academic institutions that allows for 200gb of storage, it does require subscriptions for higher levels of use.
Installation & Setup
wandb can be installed using pip.
pip install wandb
You need to get the API-key from the server (either cloud or local). You can do wandb login or set the environment variable WANDB_API_KEY.
export WANDB_API_KEY=<your_wandb_key>
Basic Workflow
The basic workflow for using Weights & Biases (wandb) for experiment tracking, particularly focusing on logging hyperparameters and metrics during machine learning training:
1. Initialization
- wandb.init()
- Start a wandb session to create a new run.
- Specify your project name and optionally a run name.
- Set hyperparameters using the
configargument.
2. Configuration (Hyperparameters)
- wandb.config
- After initializing with
wandb.init(), your hyperparameters are stored inwandb.config. - Hyperparameters can include learning rate, epochs, batch size, and model architecture details.
- After initializing with
3. Logging Metrics
- wandb.log()
- Log metrics like loss, accuracy, precision, recall, or any custom metrics at each training step or epoch.
- Metrics logged are sent in real-time to your wandb dashboard.
4. Saving Artifacts
- wandb.save()
- Save model checkpoints or other artifacts, ensuring reproducibility and easy retrieval.
- Typically called after training completes or at checkpoints during training.
5. Visualizing and Managing Experiments
- Go to the wandb dashboard to visualize:
- Training curves, parameter sweeps, confusion matrices, or images.
- Compare multiple runs to identify best-performing models and parameter configurations.
6. Completing the Run
- wandb.finish()
- Explicitly signal the end of your run, closing the wandb session.
This workflow ensures efficient tracking, management, and reproducibility of machine learning experiments using wandb.
Logging with WandB
We use the same MNIST training as for the MLFlow tutorial.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn, torch.optim as optim
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as T
import wandb
# Initialize wandb
wandb.init(project="mnist-pytorch", config={
"learning_rate": 1e-3,
"epochs": 5,
"batch_size": 64,
"architecture": "SimpleMLP"
})
# Model definition
class SimpleMNIST(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(28*28, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 10),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
# Data loaders
transform = T.Compose([T.ToTensor(), T.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))])
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform
), batch_size=wandb.config.batch_size, shuffle=True
)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform
), batch_size=1000
)
# Hyperparameters
lr, epochs = wandb.config.learning_rate, wandb.config.epochs
# Model setup
model = SimpleMNIST().to('cuda')
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(1, epochs+1):
# Training
model.train()
train_loss = train_acc = 0
for x, y in train_loader:
x, y = x.cuda(), y.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits = model(x)
loss = criterion(logits, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss += loss.item() * x.size(0)
train_acc += (logits.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().item()
train_loss /= len(train_loader.dataset)
train_acc /= len(train_loader.dataset)
# Validation
model.eval()
val_loss = val_acc = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in val_loader:
x, y = x.cuda(), y.cuda()
logits = model(x)
val_loss += criterion(logits, y).item() * x.size(0)
val_acc += (logits.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().item()
val_loss /= len(val_loader.dataset)
val_acc /= len(val_loader.dataset)
# Log metrics to wandb
wandb.log({
"epoch": epoch,
"train_loss": train_loss,
"train_accuracy": train_acc,
"val_loss": val_loss,
"val_accuracy": val_acc
})
print(f"Epoch {epoch}: train_loss={train_loss:.4f}, train_acc={train_acc:.4f},"
f" val_loss={val_loss:.4f}, val_acc={val_acc:.4f}")
# Save the trained model
model_path = "mnist_model.pth"
torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
wandb.save(model_path)
wandb.finish()
This has the following output
$ python ./mnist_wandb.py
wandb: Currently logged in as: mochan to http://localhost:8080. Use `wandb login --relogin` to force relogin
wandb: Tracking run with wandb version 0.20.1
wandb: Run data is saved locally in <------>
wandb: Run `wandb offline` to turn off syncing.
wandb: Syncing run balmy-cherry-1
wandb: ⭐️ View project at http://localhost:8080/mochan/mnist-pytorch
wandb: 🚀 View run at http://localhost:8080/mochan/mnist-pytorch/runs/u3mjb0ig
Epoch 1: train_loss=0.3794, train_acc=0.8894, val_loss=0.2558, val_acc=0.9239
Epoch 2: train_loss=0.1947, train_acc=0.9424, val_loss=0.1534, val_acc=0.9549
Epoch 3: train_loss=0.1421, train_acc=0.9577, val_loss=0.1222, val_acc=0.9633
Epoch 4: train_loss=0.1137, train_acc=0.9658, val_loss=0.1123, val_acc=0.9661
Epoch 5: train_loss=0.0977, train_acc=0.9707, val_loss=0.1010, val_acc=0.9694
wandb:
wandb:
wandb: Run history:
wandb: epoch ▁▃▅▆█
wandb: train_accuracy ▁▆▇██
wandb: train_loss █▃▂▁▁
wandb: val_accuracy ▁▆▇▇█
wandb: val_loss █▃▂▂▁
wandb:
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: epoch 5
wandb: train_accuracy 0.97068
wandb: train_loss 0.09774
wandb: val_accuracy 0.9694
wandb: val_loss 0.10098
wandb:
wandb: 🚀 View run balmy-cherry-1 at: http://localhost:8080/mochan/mnist-pytorch/runs/u3mjb0ig
wandb: ⭐️ View project at: http://localhost:8080/mochan/mnist-pytorch
wandb: Synced 6 W&B file(s), 0 media file(s), 0 artifact file(s) and 1 other file(s)
wandb: Find logs at: ./wandb/run-20250629_125419-u3mjb0ig/logs
In the website, we can see the run.
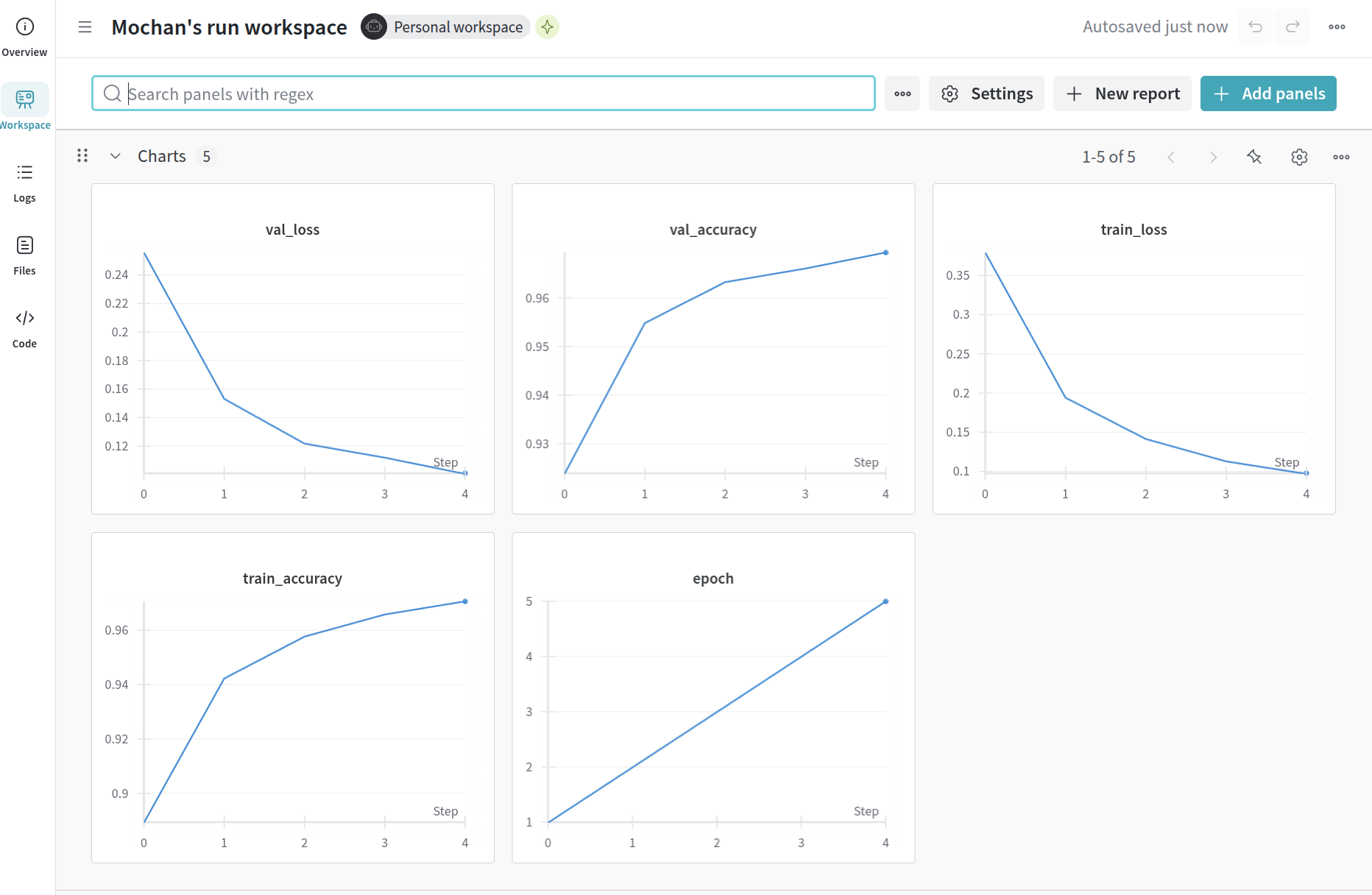
Once clicking through, you can see the metrics.
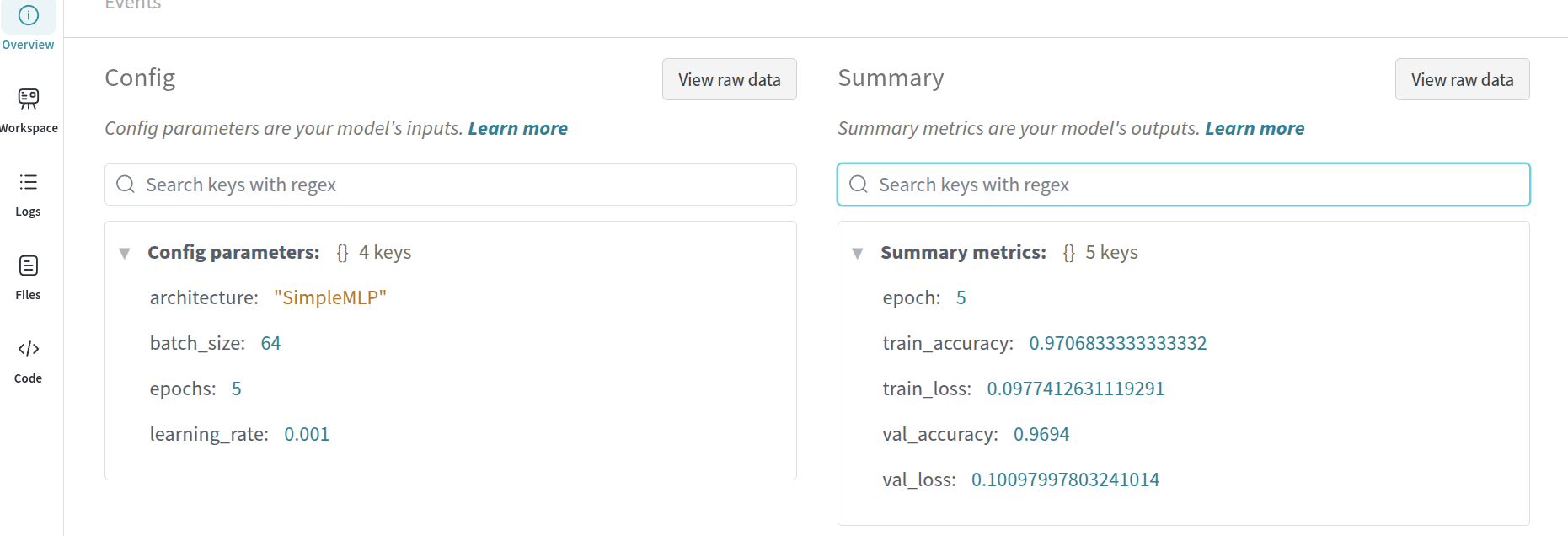
The overview section has the config parameters.
Conclusion
The code is given in the repository here.
This is a brief tutorial to get the basics of running Weights & Biases (wandb) running to log hyper parameters and store metrics.
